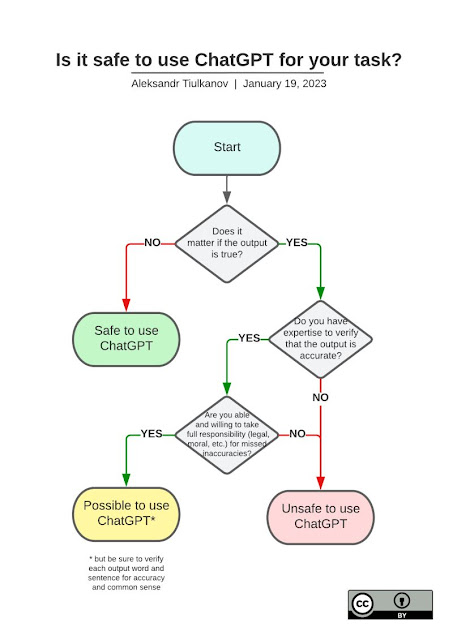
The infographic from AI, data, and digital policy expert, Aleksandr Tiulkanov helps us think about the process for using AI-generated content. Essentially, it says that if we are using AI generated content, we must know how to verify and take responsibility for the output. That means fact-checking, cross-referencing, and validating the content is essential. Innovative educators understand that they must know how to do this for ourselves as well as teach our students how to take full-responsibility for the outputs they share.
Here are some ways innovative educators can support students in developing the expertise to verify the accuracy of the content produced by generative AI.
Understand the Capabilities and Limitations of AI
Generative AI models are powerful but they don't 'understand' information or 'know' facts in the same way humans do. They generate text based on patterns they have learned from vast amounts of data and can't access real-time or updated information. This means they might produce information that is out of date, incorrect, and inconsistent.
Realize the Output May not Be Current
An AI's training data defines its knowledge. When assessing the validity of the information provided by an AI, take into account its last training data update. For example, as of now, a tool like ChatGPT is trained on a diverse range of digital text through 2021. While that will certainly change in the future, for now, it is important to be aware this affects the output we will see and how we interact with this tool. For example, you wouldn’t want to ask it about rapidly evolving topics like today’s news or current events.
Cross-reference with Reliable Sources
When looking at any content, it’s important to cross-reference information with credible sources. This is especially true when it comes to AI-generated content. If an AI produces a piece of information, especially something critical or unexpected, it's good practice to verify this information with trusted news outlets, scientific journals, or websites you’ve come to trust. Use critical thinking skills and digital literacy to discern credible sources from less reliable ones.
Use Fact-Checking Tools
There are many online tools that can help with fact-checking. Websites like Snopes, FactCheck.org, and Politifact have made it their mission to verify claims and debunk misinformation. Utilize these resources to confirm the veracity of the information AI provides.
Scrutinize for Bias
While AI models are designed to be neutral, they can sometimes reflect biases present in their training data. They may overrepresent certain viewpoints or under represent others, depending on the sources they were trained on. It's crucial to remain critical of the information you're consuming and consider whether it might be presenting a skewed perspective.
Teach Students Using Lessons & Tools
Common Sense Education has curated lessons and tools to help teach students about artificial intelligence. They've also put together guidance on how to handle artificial intelligence in schools. Become familiar with these lessons, tools, and guidance to build your comfort with supporting students in using artificial intelligence.
While generative AI has revolutionized the way we engage with digital content, they are tools, not infallible oracles. As users and educators, we must remain vigilant in helping our students understand how to cultivate their digital literacy skills and critically engage with AI-generated content.
By understanding the capabilities and limitations of AI, identifying the source of the information, cross-referencing with reliable sources, scrutinizing for bias, and using fact-checking tools, we can help students responsibly navigate this new era of AI content generation. This way, we ensure that we are supporting students in utilizing AI as a helpful tool in our quest for knowledge, rather than becoming passive consumers of AI-generated information.